Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Uchida, Shunsuke*; Hanawa, Satoshi; Naito, Masanori*; Okada, Hidetoshi*; Lister, D. H.*
Corrosion Engineering, Science and Technology, 52(8), p.587 - 595, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:21.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Based on the relationship among ECP, metal surface conditions, exposure time and other environmental conditions, a model to evaluate the ECP and corrosion rate of steel was developed by coupling a static electrochemical analysis and a dynamic oxide layer growth analysis. Major conclusion obtained on the model are as follows. The effect of H O
O and O
and O concentrations on ECP were successfully explained as the effects of oxide layer growth. Hysteresis of ECP under changes in water chemistry conditions were successfully explained with the model. Decreases in ECP due to neutron exposure were explained well by radiation-induced diffusion in the oxide layers.
concentrations on ECP were successfully explained as the effects of oxide layer growth. Hysteresis of ECP under changes in water chemistry conditions were successfully explained with the model. Decreases in ECP due to neutron exposure were explained well by radiation-induced diffusion in the oxide layers.
Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao
Photon Factory Activity Report 2016, 2 Pages, 2017/00
In order to elucidate the adsorption states of radioactive Sr-90 in soil, chemical bonding states of non-radioactive strontium adsorbed on layered oxide (mica) have been investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy. Since the number of atoms in radioactive Sr-90 is extremely small, the XPS and XANES were measured under total reflection condition of the incident X-rays. The detection limit in total reflection XPS was about 150 pg/cm , which corresponds to 300 Bq of Sr-90. The Sr 2p
, which corresponds to 300 Bq of Sr-90. The Sr 2p core-level energy in XPS shifted to lower energy with the decrease in the thickness of Sr layer. Also, the Sr 2p
core-level energy in XPS shifted to lower energy with the decrease in the thickness of Sr layer. Also, the Sr 2p
 Sr 4d
Sr 4d resonance energy in XANES shifts to lower energy with the decrease in the thickness. On the basis of a simple point charge model, it was elucidated that the chemical bond between Sr and mica surface becomes ionic with the decrease in the adsorbed amount of strontium.
resonance energy in XANES shifts to lower energy with the decrease in the thickness. On the basis of a simple point charge model, it was elucidated that the chemical bond between Sr and mica surface becomes ionic with the decrease in the adsorbed amount of strontium.
Komiyama, Daisuke; Amaya, Masaki
JAEA-Research 2016-013, 20 Pages, 2016/08
The boric acid in the coolant may precipitate on the fuel cladding surface in the case that the blockage of coolant flow path etc. occurs and/or the cooling of fuel becomes insufficient during a LOCA (Loss-Of-Coolant Accident) in PWRs. While there is much knowledge about the compatibility between Zircaloy-4 and boric acid under normal operation conditions, such knowledge under high temperature condition, e.g. LOCA, has not been sufficient. In this study, isothermal heating tests were carried out by using Zircaloy-4 plates with solid boric acid in various atmospheres at up to 900 C; and the stability of boric acid, the reaction between Zircaloy-4 and boric acid and the effect of solid boric acid on the high temperature oxidation behavior of Zircaloy-4 were investigated. From the results obtained, it was suggested that, if boric acid anhydride remained on the surface of Zircaloy-4, the boric acid anhydride prevented the surface of Zircaloy-4 from contacting oxidizing atmosphere and mitigated the high-temperature oxidation of Zircaloy-4. In the case that solid boric acid adhered to the surface of pre-oxidized Zircaloy-4 and they have been heated up to high temperature, it was indicated that the solid boric acid penetrated into the gaps in the pre-oxide layer and the penetrated solid boric acid mitigated the oxidation of Zircaloy-4 thereafter.
C; and the stability of boric acid, the reaction between Zircaloy-4 and boric acid and the effect of solid boric acid on the high temperature oxidation behavior of Zircaloy-4 were investigated. From the results obtained, it was suggested that, if boric acid anhydride remained on the surface of Zircaloy-4, the boric acid anhydride prevented the surface of Zircaloy-4 from contacting oxidizing atmosphere and mitigated the high-temperature oxidation of Zircaloy-4. In the case that solid boric acid adhered to the surface of pre-oxidized Zircaloy-4 and they have been heated up to high temperature, it was indicated that the solid boric acid penetrated into the gaps in the pre-oxide layer and the penetrated solid boric acid mitigated the oxidation of Zircaloy-4 thereafter.
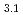 (OCOCH
(OCOCH )
)
 0.9H
0.9H O
OKozai, Naofumi; Mitamura, Hisayoshi; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu; Esaka, Fumitaka; Komarneni, S.*
Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 89(1-3), p.123 - 131, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:39.24(Chemistry, Applied)Layered transition metal hydroxide salt (LTMHS) is a group of anion-exchangeable layered compounds. Although LTMHSs have recentely attracted attention of researches on anion exchange and intercalation, very limited numbers of reports have been published on their synthesis, characteristics, and applications. This paper describes basic characteristics of a new LTMHS, nickel-copper hydroxide acetate. Hydrothermal Heating of an aqueous solution containing nickel acetate, copper acetate, and hydrogen peroxide to 150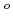 C for 4h yielded a layered compound with an analytical composition of NiCu(OH)
C for 4h yielded a layered compound with an analytical composition of NiCu(OH)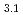 (OCOCH
(OCOCH )
) 0.9H
0.9H O. This compound does not take up Cl
O. This compound does not take up Cl and NO
and NO
 in aqueous solution but takes up multivalent anions and shows high selectivity in uptake of toxic SeO
in aqueous solution but takes up multivalent anions and shows high selectivity in uptake of toxic SeO
 and AsO
and AsO
 . This compound may find applicarion in the removal of those toxic anions form natural water and wastewater rich in Cl
. This compound may find applicarion in the removal of those toxic anions form natural water and wastewater rich in Cl and NO
and NO
 .
.
Kozai, Naofumi; Mitamura, Hisayoshi; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu; Esaka, Fumitaka; Komarneni, S.*
Journal of Materials Research, 20(11), p.2997 - 3003, 2005/11
Layered transition metal hydroxide salt (LTMHS) is a group of anion-exchangeable layered compounds. LTMHSs have lately attraced attention of researchs on anion exchange and intercalation but very limited numbers of reports have been published on their synthesis, characteristics, and application. This study reports basic properties of a layered copper hyroxide acetate synthesized by a method modified from that of the previous studies. Titration of copper acetate solution with a dilute NaOH solution to pH 6.5 and subsequent aging at 313 K yielded a layered copper hydroxide acetate. This compound has some properties similar to those of the previously known copper hydroxide acetate, Cu (OH)
(OH) (OCOCH
(OCOCH )H
)H O. The present copper hydroxide acetate is dissimilar to the previous compound in morphology, stability of bonding between the interlayer acetate ions and the matrix hydroxides, and reaction with anions in aqueous solutions.
O. The present copper hydroxide acetate is dissimilar to the previous compound in morphology, stability of bonding between the interlayer acetate ions and the matrix hydroxides, and reaction with anions in aqueous solutions.
Takakuwa, Yuji*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
Shokubai, 47(5), p.352 - 357, 2005/08
Oxidation reactions of Ti(0001) surfaces were monitored by real-time photoelectron spectroscopy with high brilliant synchrotron radiation and He-I resonance line. An oxygen adsorption model and ultra-thin oxide layers formation processes were reviewed on the basis of time evolutions of the adsorbed oxygen amount, oxidation states, electronic states and the work function, which were obtained from photoelectron spectra for Ti 2p and O 1s core levels as well as the valence band.
Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Hirabayashi, Takakuni*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(9), p.919 - 924, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:61.44(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new laser decontamination method utilizing a gel made from a sodium silicate solution and an acid was developed for removing radioactive nuclide incorporated into a surface oxide layer on metal waste. Decontamination tests were carried out using both simulated contaminated samples and pipe specimens cut from the primary coolant system of the Japan Power Demonstration Reactor. In the case of surface oxide layer consisting mainly of iron oxide, more than 99% of surface radioactivities were removed after two to three decontamination runs. In order to ascertain the role of laser irradiation on chemical reactions, chemical states of O and Fe in the oxide layer before and after decontamination were analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. It was found that the oxide layer was dissolved into the acid-containing gel, and the reaction was extensively promoted by the laser irradiation.
Teraoka, Yuden
Denki Gakkai Gijutsu Hokoku, (970), p.10 - 15, 2004/07
Si(001) surfaces are oxidized by O molecules. The reaction schemes (oxide-layers formation, SiO desorption, their coexistence) are changed depending on the surface temperature and the gas pressure. The translational kinetic energy of incident O
molecules. The reaction schemes (oxide-layers formation, SiO desorption, their coexistence) are changed depending on the surface temperature and the gas pressure. The translational kinetic energy of incident O molecules is recognizing to be an important parameter for controlling surface chemical reactions. The issues concerning translational kinetic energy induced oxidation by O
molecules is recognizing to be an important parameter for controlling surface chemical reactions. The issues concerning translational kinetic energy induced oxidation by O molecules at room temperature, effects of translational kinetic energy for SiO desorption processes at higher temperature than 1000 K, reaction mechanisms for coexistence of the SiO desorption and the oxide-layers formation in the temperature region from 900 K to 1000 K are reviewed.
molecules at room temperature, effects of translational kinetic energy for SiO desorption processes at higher temperature than 1000 K, reaction mechanisms for coexistence of the SiO desorption and the oxide-layers formation in the temperature region from 900 K to 1000 K are reviewed.
The Working Team for Examination Operation of Samples From Core Shroud at Fukushima Dai-ni Unit-3
JAERI-Tech 2004-044, 92 Pages, 2004/05
The present examination has been performed with the objective to ensure the transparency of the examination as the third-party organization by providing technical basis for identifying the causes of cracking through examination of the sample taken from the cracked region of outer H6a welding portion of the core shroud at Fukushima Dai-ni Nuclear Power Station Unit-3, which was a part of sample stored in the Nippon Nuclear Fuel Development Co., Ltd. in the examination of Tokyo Electric Power Company in 2001. The present examination of the sample was conducted at the post irradiation examination facilities of JAERI. The following findings were obtained from the result of the present examination. (1)Three cracks were observed at the portion 3 to 9mm apart from the weld metal and the maximum depth was about 8mm. (2)Intergranular cracking was observed in almost whole fracture surface. The transgranular cracking was partially observed within the depth of about 300 m from the surface. (3)Hardening layer over Hv400 at its maximum was found from the surface to the depth of about 500
m from the surface. (3)Hardening layer over Hv400 at its maximum was found from the surface to the depth of about 500 m. Based on the examination results concerning presence of tensile residual stress by welding and relatively high dissolved oxygen contents in core coolant, it is concluded that the cracks were mainly initiated in the hardening layer by transgranular stress corrosion cracking and propagated along the grain boundaries.
m. Based on the examination results concerning presence of tensile residual stress by welding and relatively high dissolved oxygen contents in core coolant, it is concluded that the cracks were mainly initiated in the hardening layer by transgranular stress corrosion cracking and propagated along the grain boundaries.
The Working Team for Examination of the Sample from Core Shrouds and Primary Loop Recirculation Pipi; Nakajima, Hajime*; Shibata, Katsuyuki; Tsukada, Takashi; Suzuki, Masahide; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Kikuchi, Masahiko; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Nakano, Junichi; et al.
JAERI-Tech 2004-015, 114 Pages, 2004/03
The Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) visually inspected the weld joint of core shroud at Fukushima Dai-ni Nuclear Power Station Unit-2 by a direction of the Nuclear and Industrial Agency, cracks were observed at outer side of the ring weld joint (H3) between a core shroud middle trunk and a middle ring. TEPCO has conducted a material examination with Nippon Nuclear Fuel Development Co. Ltd. (NFD) on the specimen including cracks sampled from the core shroud. The present examination has been performed with the objective to independently investigate and evaluate the materials by jointly attending the examination with NFD from the planning stage. Based on results of the present examination, the probable presence of tensile residual stress by welding process and dissolved oxygen contents in the cooling water, it was shown that the cracks were considered to be stress corrosion cracking (SCC). However, the cause of the cracks needs more consideration on the way of shroud construction.
The Working Team for Examination of the Sample from Core Shrouds and Primary Loop Recirculation Pipi
JAERI-Tech 2004-012, 62 Pages, 2004/02
At Onagawa Nuclear Power Station Unit-1 of the Tohoku Electric Power co., inc., cracks were confirmed near welded joints of core shroud in 15th periodical inspection. Tohoku Electric Power co., inc. has conducted a material examination with Nippon Nuclear Fuel Development Co., Ltd.. To investigate independently, a JAERI's own evaluation report was provided. The results are as follows; (1) Hardening layer was detected at the depth of about 150-250 m from outer surface of the sample. (2) Corrosion products were observed on inner surface of the cracks and some of them penetrated into grains. (3) Transgranular cracking and intergranular cracking were observed at the region within about 100
m from outer surface of the sample. (2) Corrosion products were observed on inner surface of the cracks and some of them penetrated into grains. (3) Transgranular cracking and intergranular cracking were observed at the region within about 100 m and the deeper region more than about 200
m and the deeper region more than about 200 m in depth from outer surface of the sample, respectively. (4) Distinct chromium depletion was not detected at the grain boundaries. (5) Chemical compositions of the sample corresponded to type 304L stainless steel in Japanese Industrial Standard. From the above, it is concluded that the cracks are stress corrosion cracking.
m in depth from outer surface of the sample, respectively. (4) Distinct chromium depletion was not detected at the grain boundaries. (5) Chemical compositions of the sample corresponded to type 304L stainless steel in Japanese Industrial Standard. From the above, it is concluded that the cracks are stress corrosion cracking.
The Working Team for Examination of the Sample from Core Shrouds and Primary Loop Recirculation Pipi
JAERI-Tech 2004-011, 64 Pages, 2004/02
At the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station Unit-1 of the TEPCO, cracks were confirmed at the weld joint (H4) in the middle of core shroud, by the visual inspection test for the weld joint of core shroud during the 13th periodic examination by a direction of the Nuclear and Industrial Agency. TEPCO has conducted a material examination with NFD on the specimen including cracks sampled from the core shroud. The present research has been performed with the objective to independently investigate and evaluate the materials by jointly attending the examination with NFD from the planning stage, receiving the final data given by the examination and providing JAERI's own evaluation report as a third-party organization for assuring the transparency. As a result, the consideration of residual stress induced with welding process and dissolved oxygen concentration in core cooling water, it was concluded that the cracks were initiated by SCC and propagated three-dimensionally through grains, and some cracks reached weld metal.
The Working Team for Examination of the Sample from Core Shrouds and Primary Loop Recirculation Pipi
JAERI-Tech 2004-004, 74 Pages, 2004/02
During the 12th periodical inspection in Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station Unit-4 (BWR, 784MW) of Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO), which has been held from September 1993 to February 1994, cracks were found at welded joints No.H4 in the core shroud middle shell. TEPCO has conducted a material examination with Nippon Nuclear Fuel Development Co. Ltd. (NFD) on the SUS304L specimen including cracks sampled from the inner surface of welded joints (H4) of the middle shell of the core shroud. The present examination has been performed with the objective to independently investigate and evaluate the materials by jointly attending the examination with NFD, receiving the final data given by the examination and providing a JAERI's own evaluation report as a third-party organization for assuring the transparency. Based on the research results described above, presence of tensile residual stress by welding and relatively high dissolved oxygen contents in core coolant, it is concluded that the cracks observed were caused by the stress corrosion cracking (SCC).
Mishima, Kaichiro*; Saito, Yasushi*
JAERI-Tech 2002-014, 83 Pages, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
Iida, Takeshi*; Tomioka, Yuichi*; Yoshimoto, Kimihiro*; Midorikawa, Masahiko*; Tsukada, Hiroyuki*; Orihara, Misao*; Hijikata, Yasuto*; Yaguchi, Hiroyuki*; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Ito, Hisayoshi; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 41(2A), p.800 - 804, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:52.26(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio; Hirabayashi, Takakuni*
Nuclear Technology, 137(2), p.139 - 146, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to apply laser ablation technique for decontamination of metal wastes contaminated with radioactive nuclides, the effect of irradiation atmospheres on removal of oxide layers on steel surfaces by laser ablation was studied. Based on the assumption that the absorption of laser light follows the Lambert-Beer law, ablation parameters, such as absorption length and threshold fluence for ablation, of sintered Fe O
O and stainless and carbon steels were measured in He, O
and stainless and carbon steels were measured in He, O , Kr or SF
, Kr or SF atmosphere. The results indicated that SF
atmosphere. The results indicated that SF was the most effective gas of all irradiation atmospheres studied for the exclusive removal of oxide layers formed on stainless and carbon steel samples in high temperature pressurized water. Secondary ion mass spectroscopic measurement and scanning electron microscopic observation confirmed that no oxide layer existed on the steel samples after the exclusive removal with laser irradiation.
was the most effective gas of all irradiation atmospheres studied for the exclusive removal of oxide layers formed on stainless and carbon steel samples in high temperature pressurized water. Secondary ion mass spectroscopic measurement and scanning electron microscopic observation confirmed that no oxide layer existed on the steel samples after the exclusive removal with laser irradiation.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asai, Keisuke*
Langmuir, 17(9), p.2564 - 2567, 2001/05
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:92.2(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)A new type of TiO nanosheet-organic complex multilayer film was successfully prepared by the Langmuir-Blodgett technique. Surface pressure-area curves demonstrated that a stable monolayer of dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide (DODAB) was formed on an aqueous suspension of TiO
nanosheet-organic complex multilayer film was successfully prepared by the Langmuir-Blodgett technique. Surface pressure-area curves demonstrated that a stable monolayer of dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide (DODAB) was formed on an aqueous suspension of TiO nanosheets derived from an exfoliated layered titanate, H
nanosheets derived from an exfoliated layered titanate, H Ti
Ti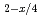 □
□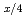 O
O ・H
・H O (x
O (x 0.7; □, vacancy). The hybrid monolayer of the ammonium amphiphiles and the TiO
0.7; □, vacancy). The hybrid monolayer of the ammonium amphiphiles and the TiO nanosheet was quantitatively transferred onto a hydrophobic quartz plate to form a multilayer film. X-ray diffraction measurements confirmed the formation of an ordered structure of DODAB/TiO
nanosheet was quantitatively transferred onto a hydrophobic quartz plate to form a multilayer film. X-ray diffraction measurements confirmed the formation of an ordered structure of DODAB/TiO with an interlayer distance of 3.4 nm.
with an interlayer distance of 3.4 nm.
JAERI-M 82-015, 21 Pages, 1982/03
no abstracts in English
; ;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 19(6), p.469 - 481, 1982/00
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ;
JAERI-M 9475, 22 Pages, 1981/05
no abstracts in English